This post is a summary of the Udacity Robotics Nanodegree Lab on localization using Monte Carlo Localization (MCL). The Udacity repo can be found here
To follow this tutorial, clone the repo to a folder of your choice.
git clone https://github.com/udacity/RoboND-MCL-Lab Monte Carlo Localization Algorithm
C++ Implementation
The following headers are used in the lab, which are mainly from the standard c++ library. One exception is the third party plotting library found here that uses python’s matplotlib as its backend.
#include "src/matplotlibcpp.h" //Graph Library
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdexcept> // throw errors
#include <random> //C++ 11 Random Numbers
#include <vector>
namespace plt = matplotlibcpp;
using namespace std;Next, some global variables are defined for the fixed landmarks and the world size.
The random generator gets initialized and a forward declaration of two functions is made, namely
mod and gen_real_random.
// Landmarks
double landmarks[8][2] = { { 20.0, 20.0 }, { 20.0, 80.0 }, { 20.0, 50.0 },
{ 50.0, 20.0 }, { 50.0, 80.0 }, { 80.0, 80.0 },
{ 80.0, 20.0 }, { 80.0, 50.0 } };
// Map size in meters
double world_size = 100.0;
// Random Generators
random_device rd;
mt19937 gen(rd());
// Global Functions
double mod(double first_term, double second_term);
double gen_real_random();Robot Base Class
The lab uses a robot class that initializes a robot with a random x and y location and orientation in its constructor.
Robot()
{
// Constructor
x = gen_real_random() * world_size; // robot's x coordinate
y = gen_real_random() * world_size; // robot's y coordinate
orient = gen_real_random() * 2.0 * M_PI; // robot's orientation
forward_noise = 0.0; //noise of the forward movement
turn_noise = 0.0; //noise of the turn
sense_noise = 0.0; //noise of the sensing
}void set(double new_x, double new_y, double new_orient)
{
// Set robot new position and orientation
if (new_x < 0 || new_x >= world_size)
throw std::invalid_argument("X coordinate out of bound");
if (new_y < 0 || new_y >= world_size)
throw std::invalid_argument("Y coordinate out of bound");
if (new_orient < 0 || new_orient >= 2 * M_PI)
throw std::invalid_argument("Orientation must be in [0..2pi]");
x = new_x;
y = new_y;
orient = new_orient;
}void set_noise(double new_forward_noise, double new_turn_noise, double new_sense_noise)
{
// Simulate noise, often useful in particle filters
forward_noise = new_forward_noise;
turn_noise = new_turn_noise;
sense_noise = new_sense_noise;
}vector<double> sense()
{
// Measure the distances from the robot toward the landmarks
vector<double> z(sizeof(landmarks) / sizeof(landmarks[0]));
double dist;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(landmarks) / sizeof(landmarks[0]); i++) {
dist = sqrt(pow((x - landmarks[i][0]), 2) + pow((y - landmarks[i][1]), 2));
dist += gen_gauss_random(0.0, sense_noise);
z[i] = dist;
}
return z;
}Robot move(double turn, double forward)
{
if (forward < 0)
throw std::invalid_argument("Robot cannot move backward");
// turn, and add randomness to the turning command
orient = orient + turn + gen_gauss_random(0.0, turn_noise);
orient = mod(orient, 2 * M_PI);
// move, and add randomness to the motion command
double dist = forward + gen_gauss_random(0.0, forward_noise);
x = x + (cos(orient) * dist);
y = y + (sin(orient) * dist);
// cyclic truncate
x = mod(x, world_size);
y = mod(y, world_size);
// set particle
Robot res;
res.set(x, y, orient);
res.set_noise(forward_noise, turn_noise, sense_noise);
return res;
}string show_pose()
{
// Returns the robot current position and orientation in a string format
return "[x=" + to_string(x) + " y=" + to_string(y) + " orient=" + to_string(orient) + "]";
}string read_sensors()
{
// Returns all the distances from the robot toward the landmarks
vector<double> z = sense();
string readings = "[";
for (int i = 0; i < z.size(); i++) {
readings += to_string(z[i]) + " ";
}
readings[readings.size() - 1] = ']';
return readings;
}double measurement_prob(vector<double> measurement)
{
// Calculates how likely a measurement should be
double prob = 1.0;
double dist;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(landmarks) / sizeof(landmarks[0]); i++) {
dist = sqrt(pow((x - landmarks[i][0]), 2) + pow((y - landmarks[i][1]), 2));
prob *= gaussian(dist, sense_noise, measurement[i]);
}
return prob;
}The class has the following public member variables
double x, y, orient; //robot poses
double forward_noise, turn_noise, sense_noise; //robot noisesIt uses the follwoing private methods
double gen_gauss_random(double mean, double variance)
{
// Gaussian random
normal_distribution<double> gauss_dist(mean, variance);
return gauss_dist(gen);
}double gaussian(double mu, double sigma, double x)
{
// Probability of x for 1-dim Gaussian with mean mu and var. sigma
return exp(-(pow((mu - x), 2)) / (pow(sigma, 2)) / 2.0) / sqrt(2.0 * M_PI * (pow(sigma, 2)));
}Global functions
Other useufl global functions
// Functions
double gen_real_random()
{
// Generate real random between 0 and 1
uniform_real_distribution<double> real_dist(0.0, 1.0); //Real
return real_dist(gen);
}
double mod(double first_term, double second_term)
{
// Compute the modulus
return first_term - (second_term)*floor(first_term / (second_term));
}
double evaluation(Robot r, Robot p[], int n)
{
//Calculate the mean error of the system
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//the second part is because of world's cyclicity
double dx = mod((p[i].x - r.x + (world_size / 2.0)), world_size) - (world_size / 2.0);
double dy = mod((p[i].y - r.y + (world_size / 2.0)), world_size) - (world_size / 2.0);
double err = sqrt(pow(dx, 2) + pow(dy, 2));
sum += err;
}
return sum / n;
}
double max(double arr[], int n)
{
// Identify the max element in an array
double max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max)
max = arr[i];
}
return max;
}Visualization
For visualization matplotlib is used as backend.
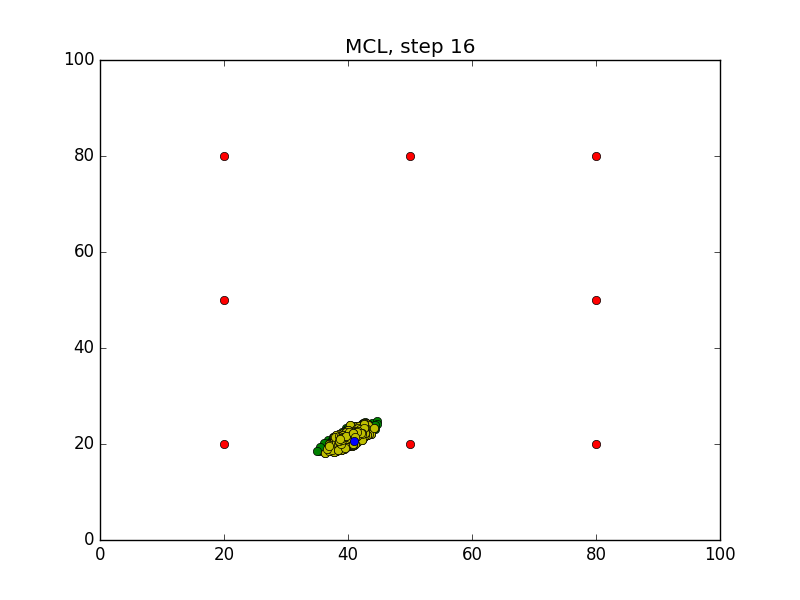
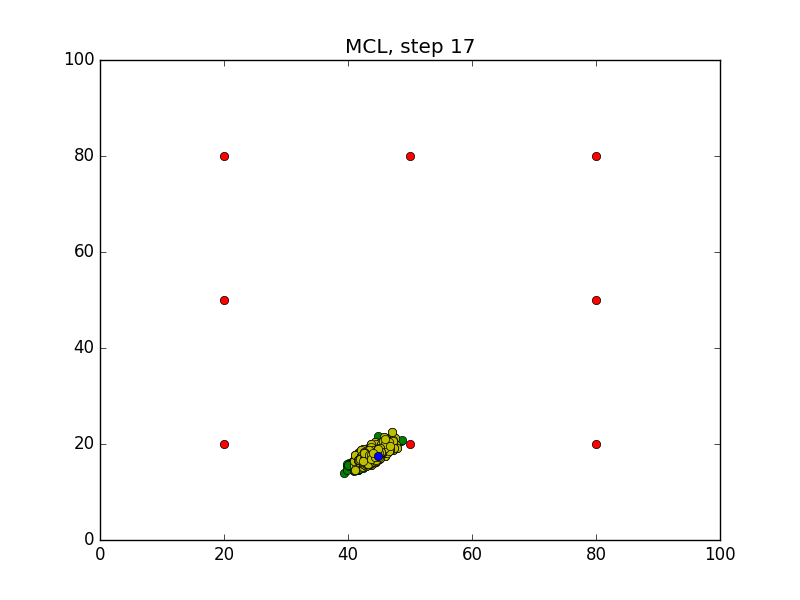
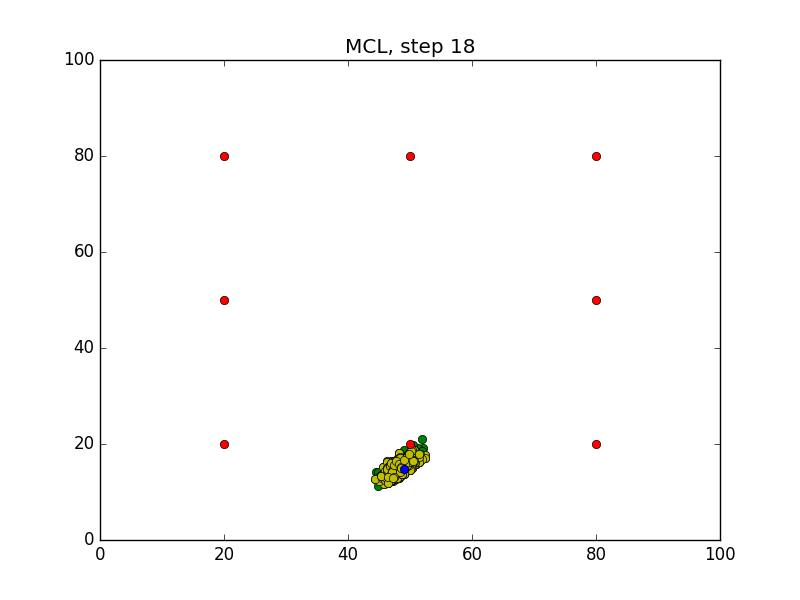
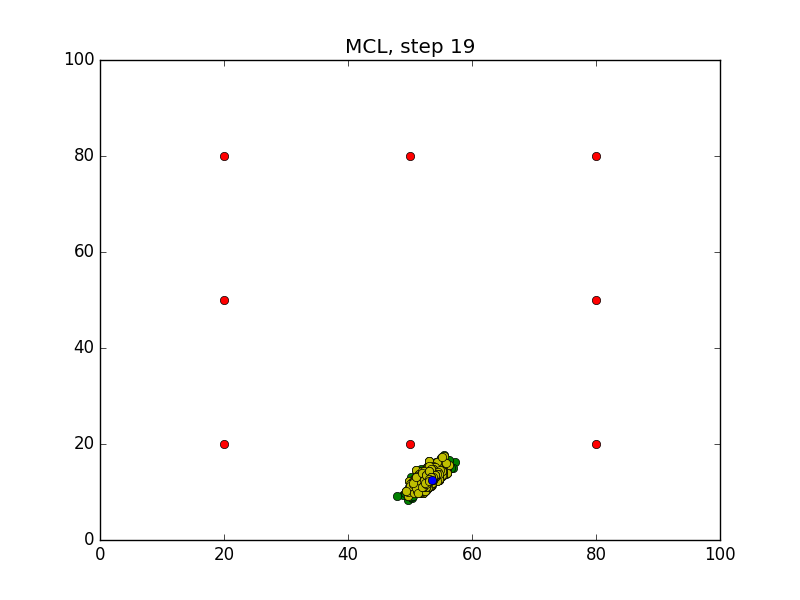
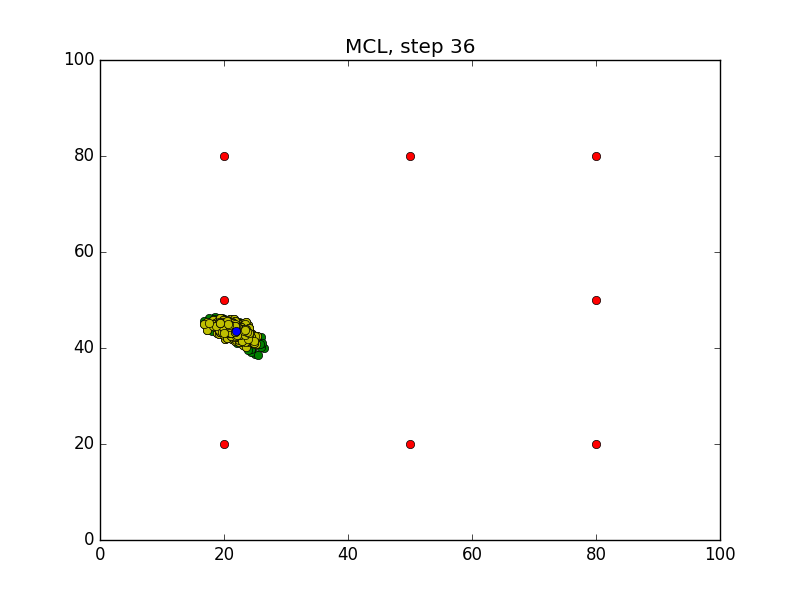
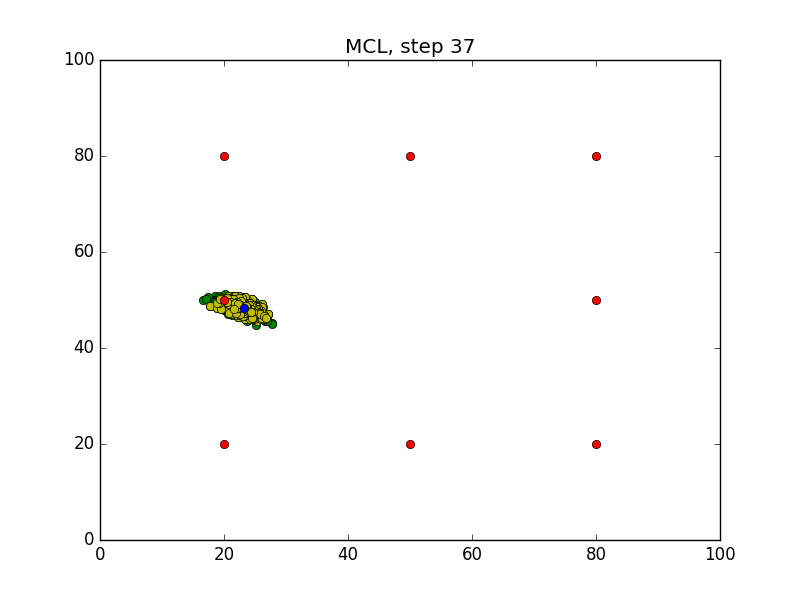
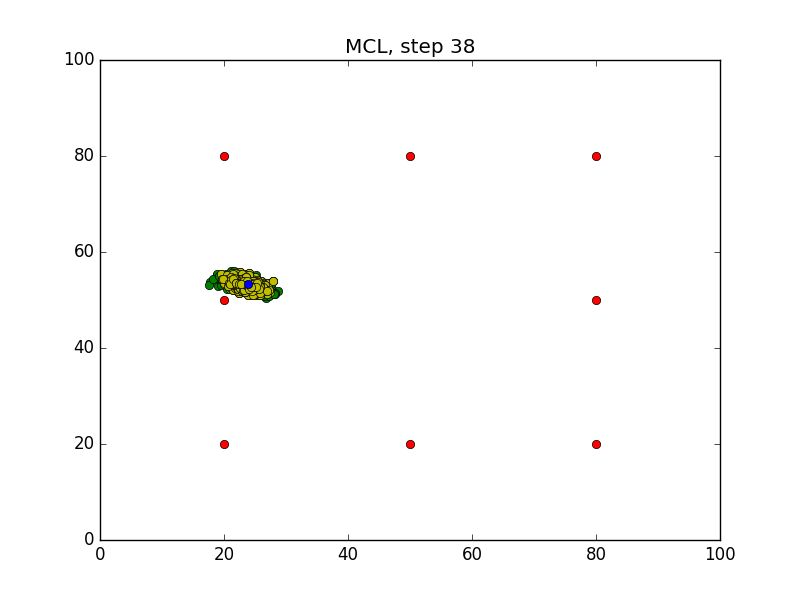
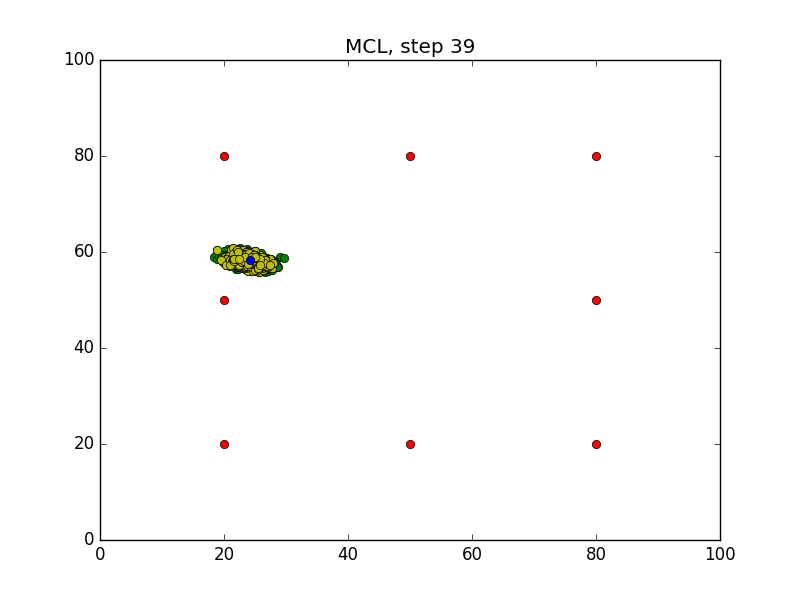
void visualization(int n, Robot robot, int step, Robot p[], Robot pr[])
{
//Draw the robot, landmarks, particles and resampled particles on a graph
//Graph Format
plt::title("MCL, step " + to_string(step));
plt::xlim(0, 100);
plt::ylim(0, 100);
//Draw particles in green
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
plt::plot({ p[i].x }, { p[i].y }, "go");
}
//Draw resampled particles in yellow
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
plt::plot({ pr[i].x }, { pr[i].y }, "yo");
}
//Draw landmarks in red
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(landmarks) / sizeof(landmarks[0]); i++) {
plt::plot({ landmarks[i][0] }, { landmarks[i][1] }, "ro");
}
//Draw robot position in blue
plt::plot({ robot.x }, { robot.y }, "bo");
//Save the image and close the plot
plt::save("./Images/Step" + to_string(step) + ".png");
plt::clf();
}Main
int main()
{
//Practice Interfacing with Robot Class
Robot myrobot;
myrobot.set_noise(5.0, 0.1, 5.0);
myrobot.set(30.0, 50.0, M_PI / 2.0);
myrobot.move(-M_PI / 2.0, 15.0);
//cout << myrobot.read_sensors() << endl;
myrobot.move(-M_PI / 2.0, 10.0);
//cout << myrobot.read_sensors() << endl;
// Create a set of particles
int n = 1000;
Robot p[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i].set_noise(0.05, 0.05, 5.0);
//cout << p[i].show_pose() << endl;
}
//Re-initialize myrobot object and Initialize a measurment vector
myrobot = Robot();
vector<double> z;
//Iterating 50 times over the set of particles
int steps = 50;
for (int t = 0; t < steps; t++) {
//Move the robot and sense the environment afterwards
myrobot = myrobot.move(0.1, 5.0);
z = myrobot.sense();
// Simulate a robot motion for each of these particles
Robot p2[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p2[i] = p[i].move(0.1, 5.0);
p[i] = p2[i];
}
//Generate particle weights depending on robot's measurement
double w[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
w[i] = p[i].measurement_prob(z);
//cout << w[i] << endl;
}
//Resample the particles with a sample probability proportional to the importance weight
Robot p3[n];
int index = gen_real_random() * n;
//cout << index << endl;
double beta = 0.0;
double mw = max(w, n);
//cout << mw;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
beta += gen_real_random() * 2.0 * mw;
while (beta > w[index]) {
beta -= w[index];
index = mod((index + 1), n);
}
p3[i] = p[index];
}
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
p[k] = p3[k];
//cout << p[k].show_pose() << endl;
}
//Evaluate the Error
cout << "Step = " << t << ", Evaluation = " << evaluation(myrobot, p, n) << endl;
//#### DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING ABOVE HERE! ENTER CODE BELOW ####
//Graph the position of the robot and the particles at each step
visualization(n, myrobot, t, p2, p3);
} //End of Steps loop
return 0;
}Compile and Run
Compile with
g++ solution.cpp -o app -std=c++11 -I/usr/include/python2.7 -lpython2.7And finally run the program with
./appThis will output:
Step = 0, Evaluation = 4.36165
Step = 1, Evaluation = 4.13259
Step = 2, Evaluation = 3.42951
Step = 3, Evaluation = 3.2404
Step = 4, Evaluation = 2.7659
Step = 5, Evaluation = 2.48962
Step = 6, Evaluation = 2.31978
Step = 7, Evaluation = 2.24096
Step = 8, Evaluation = 2.2645
Step = 9, Evaluation = 2.16855
Step = 10, Evaluation = 2.0289
Step = 11, Evaluation = 1.90762
Step = 12, Evaluation = 1.90886
Step = 13, Evaluation = 1.86255
Step = 14, Evaluation = 1.80935
Step = 15, Evaluation = 1.75033
Step = 16, Evaluation = 1.73623
Step = 17, Evaluation = 1.66427
Step = 18, Evaluation = 1.65443
Step = 19, Evaluation = 1.68175
Step = 20, Evaluation = 1.62883
Step = 21, Evaluation = 1.61669
Step = 22, Evaluation = 1.60328
Step = 23, Evaluation = 1.55554
Step = 24, Evaluation = 1.54531
Step = 25, Evaluation = 1.48853
Step = 26, Evaluation = 1.52531
Step = 27, Evaluation = 1.54713
Step = 28, Evaluation = 1.57839
Step = 29, Evaluation = 1.59364
Step = 30, Evaluation = 1.65056
Step = 31, Evaluation = 1.6718
Step = 32, Evaluation = 1.67659
Step = 33, Evaluation = 1.61774
Step = 34, Evaluation = 1.57891
Step = 35, Evaluation = 1.50999
Step = 36, Evaluation = 1.40922
Step = 37, Evaluation = 1.40538
Step = 38, Evaluation = 1.41737
Step = 39, Evaluation = 1.39369
Step = 40, Evaluation = 1.38676
Step = 41, Evaluation = 1.43119
Step = 42, Evaluation = 1.39935
Step = 43, Evaluation = 1.37321
Step = 44, Evaluation = 1.4212
Step = 45, Evaluation = 1.55304
Step = 46, Evaluation = 1.75291
Step = 47, Evaluation = 1.93479
Step = 48, Evaluation = 1.94307
Step = 49, Evaluation = 1.25727Results
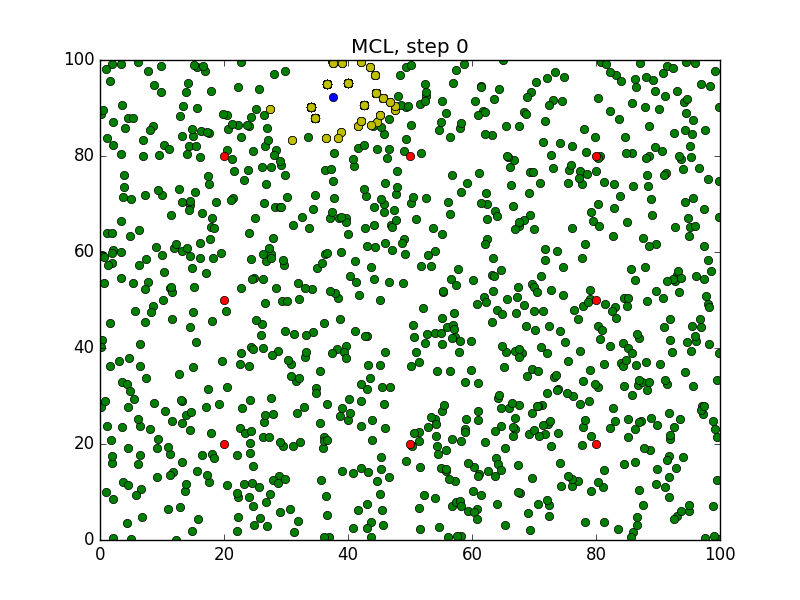
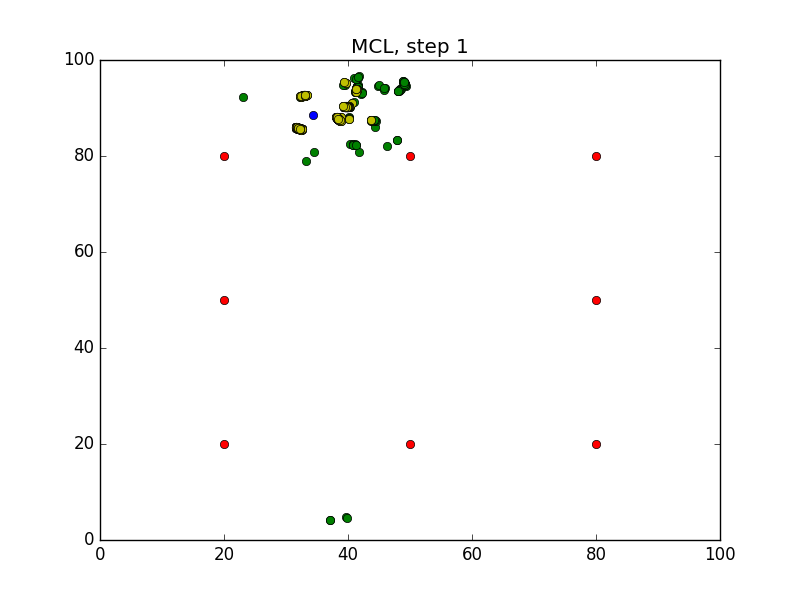
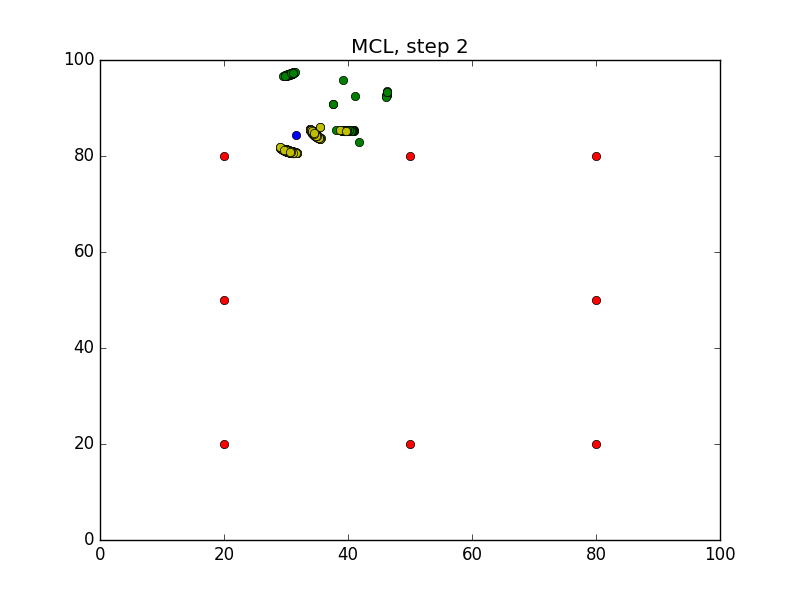
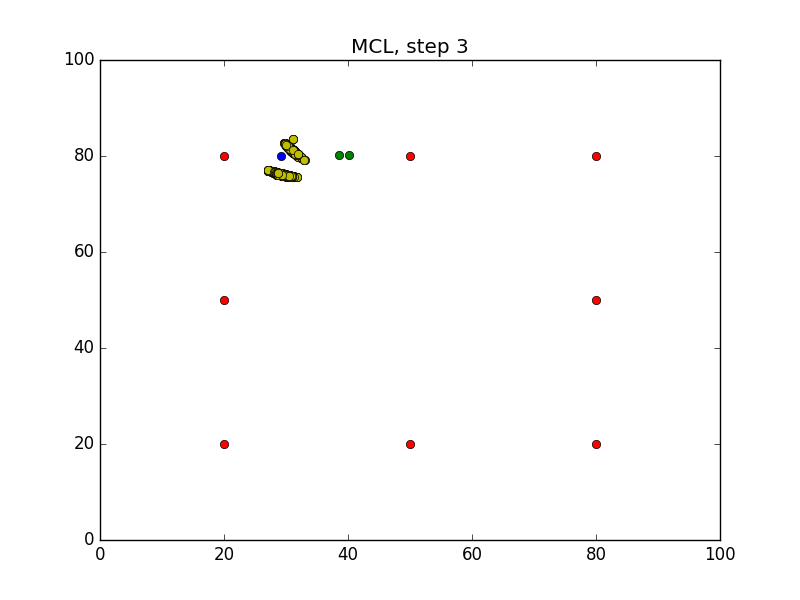
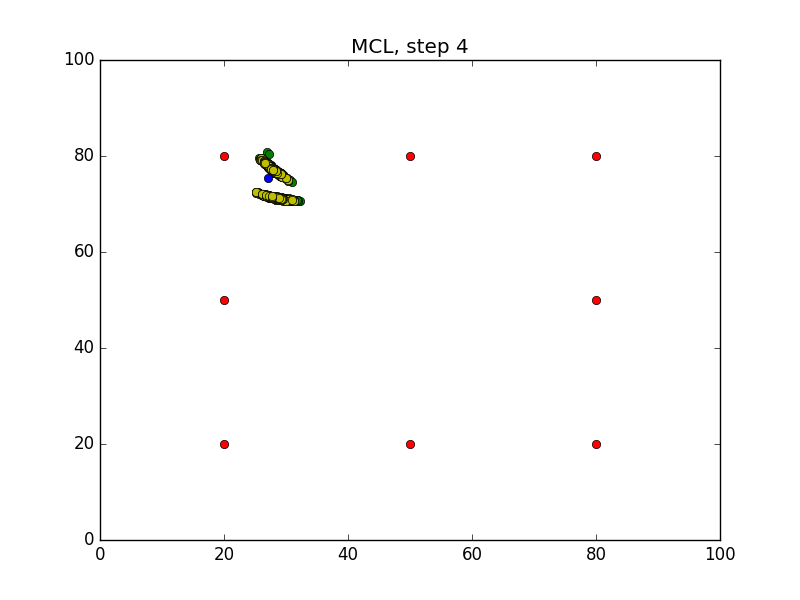
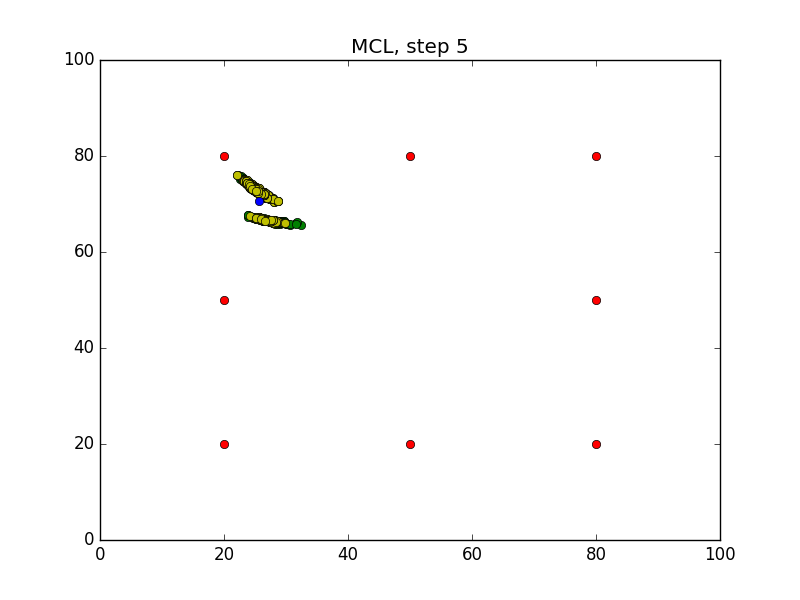
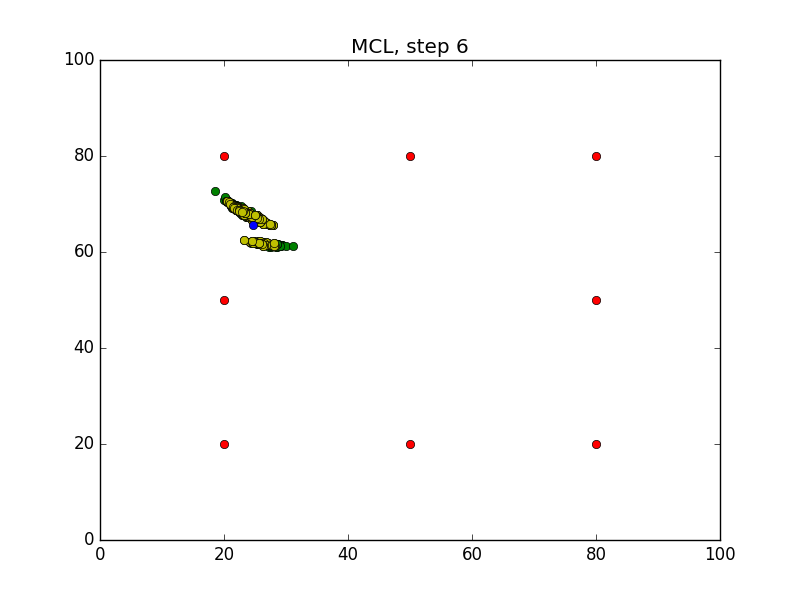
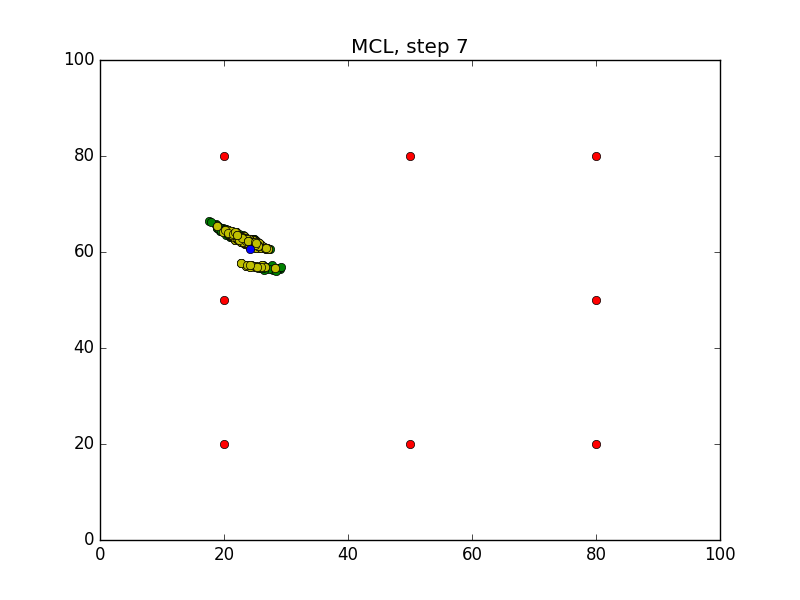
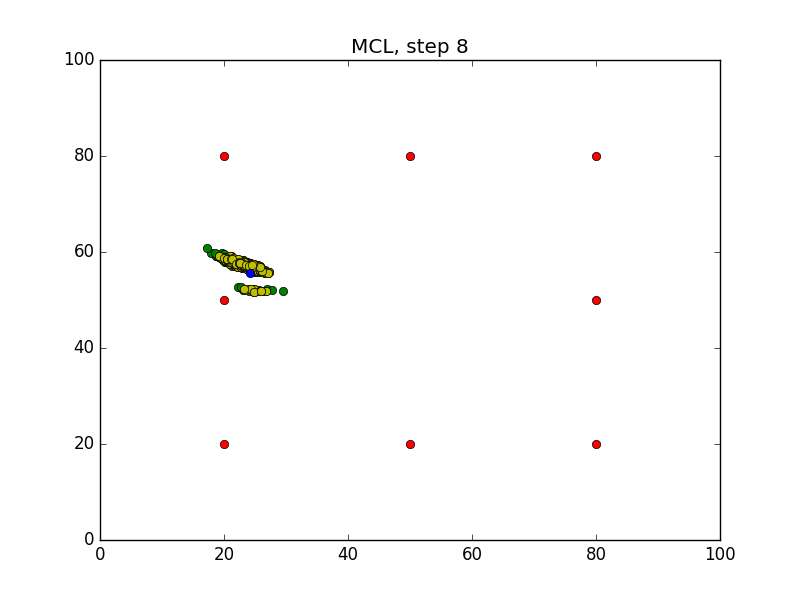
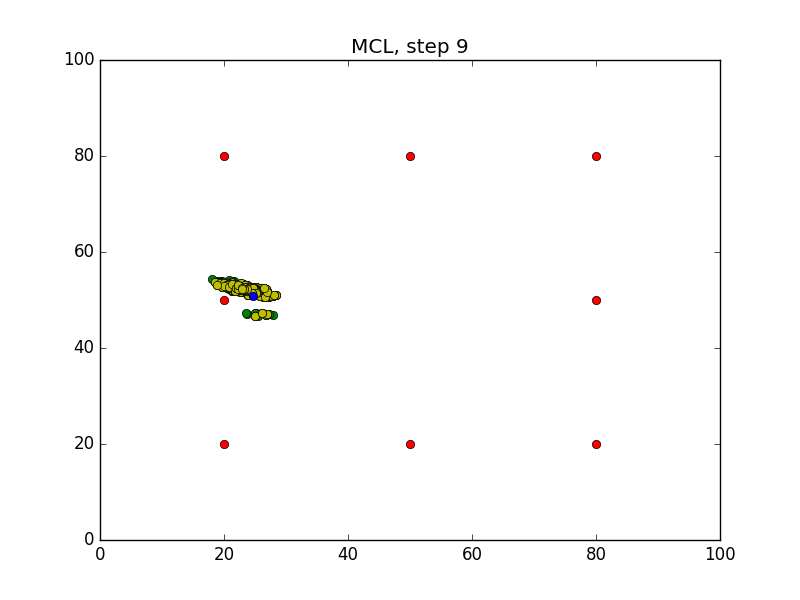
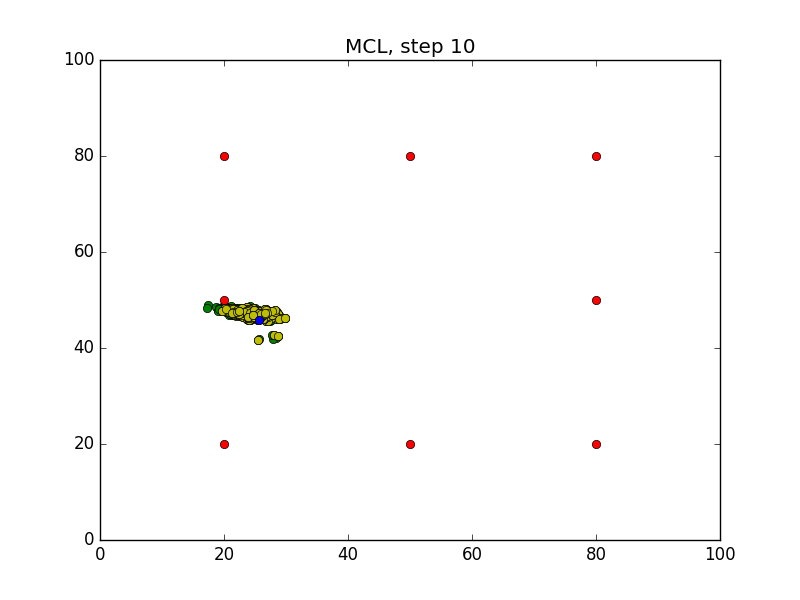
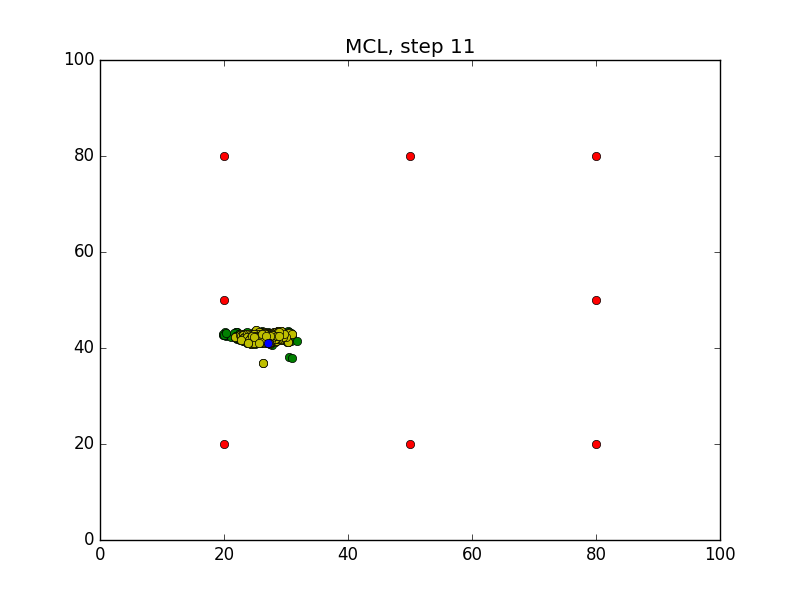
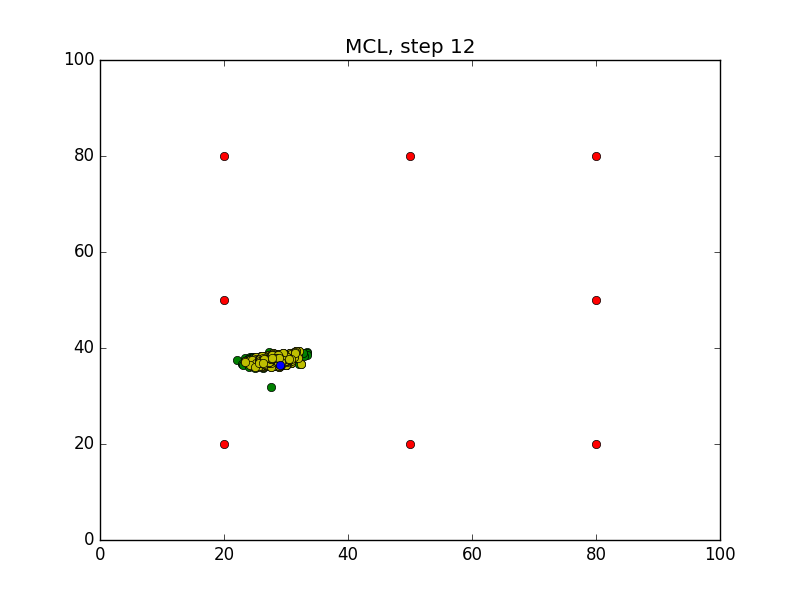
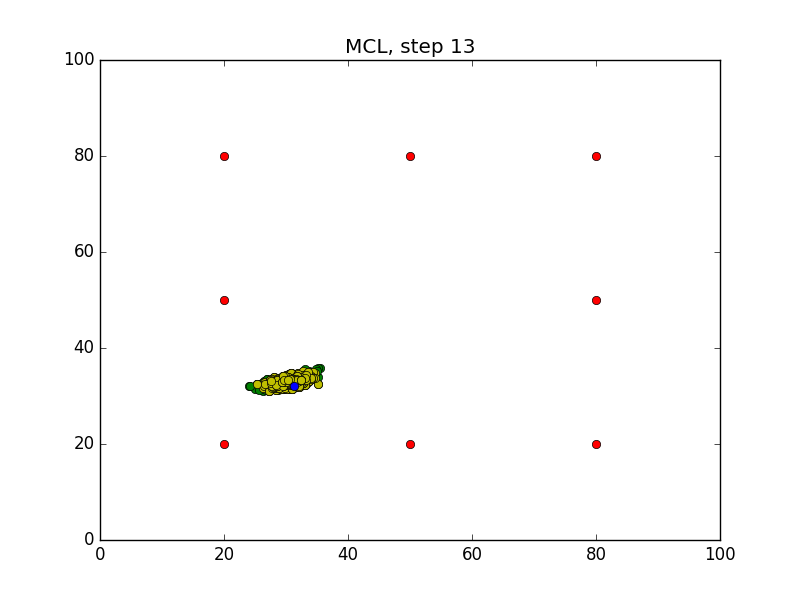
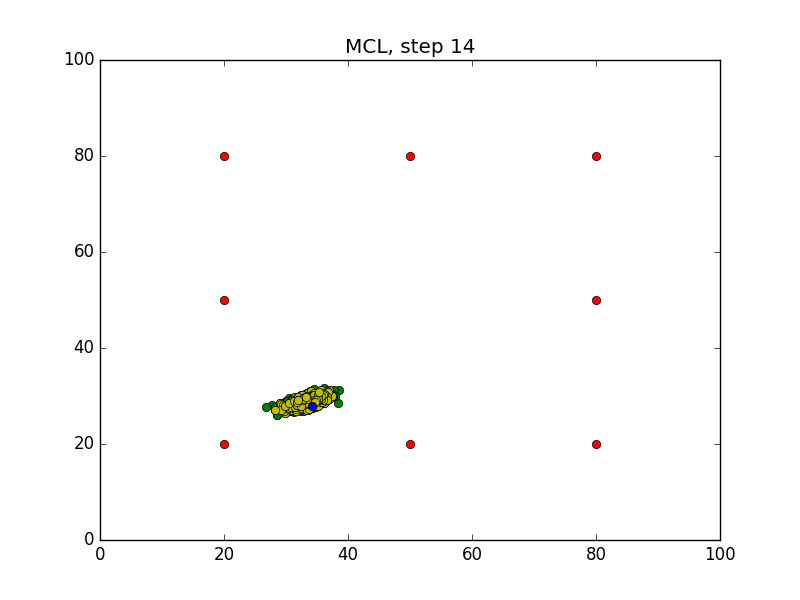
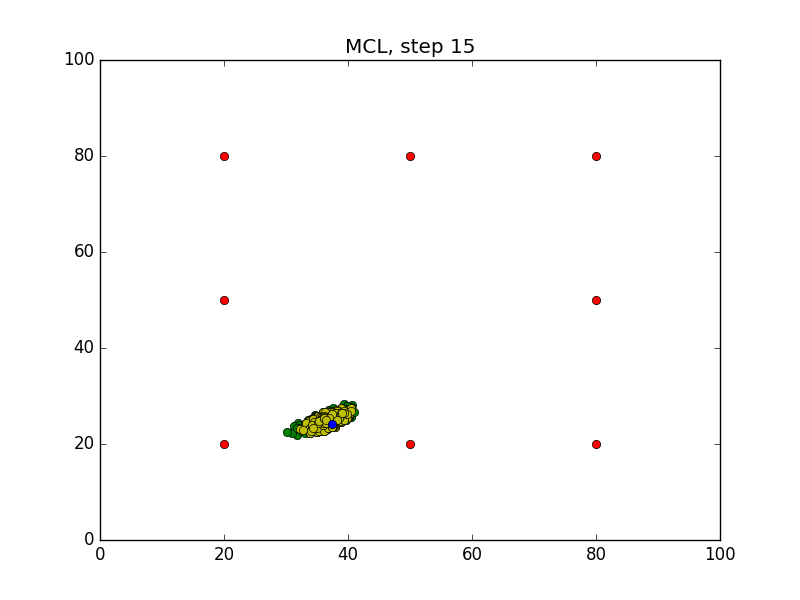
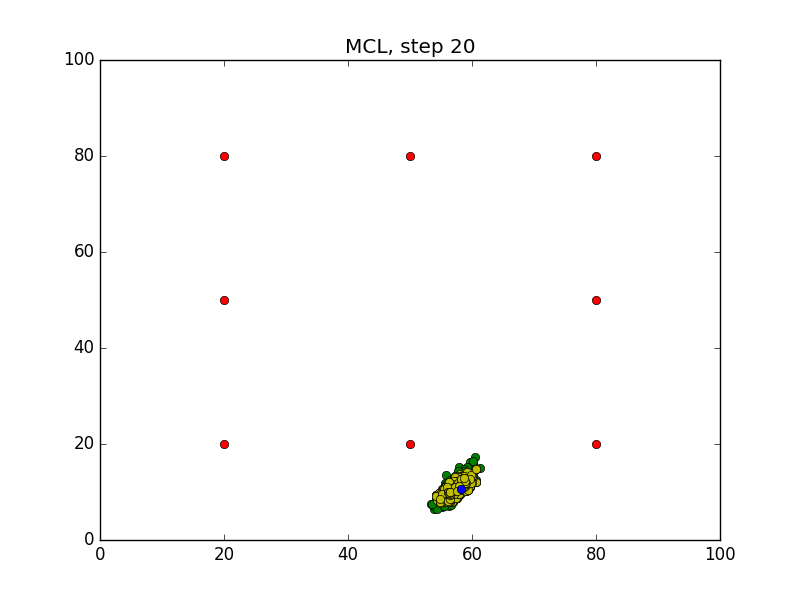
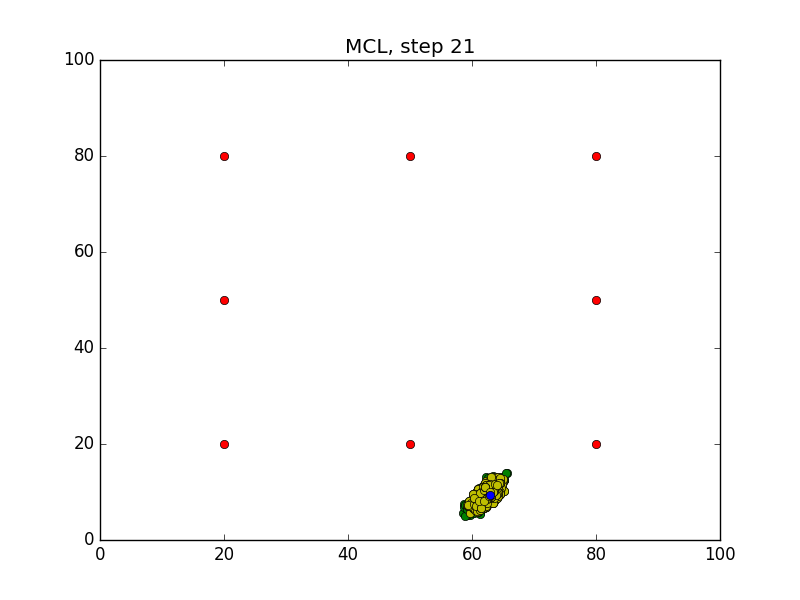
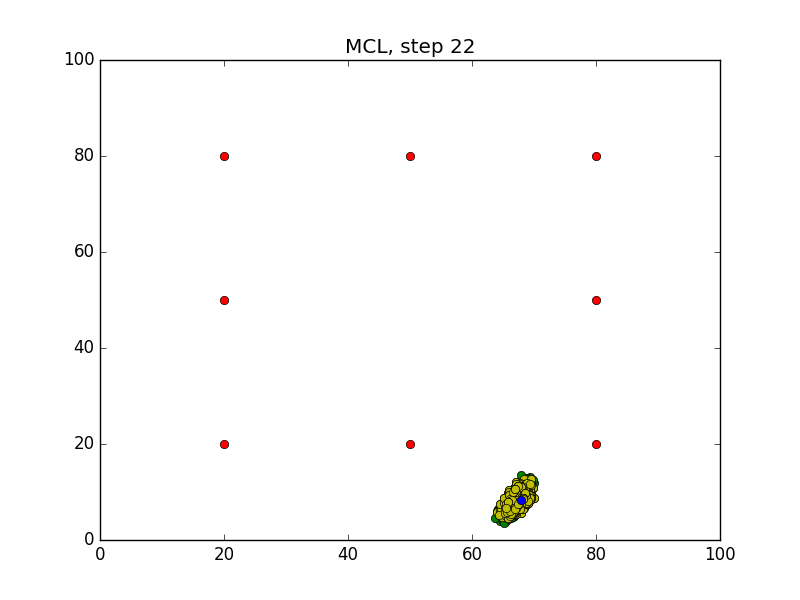
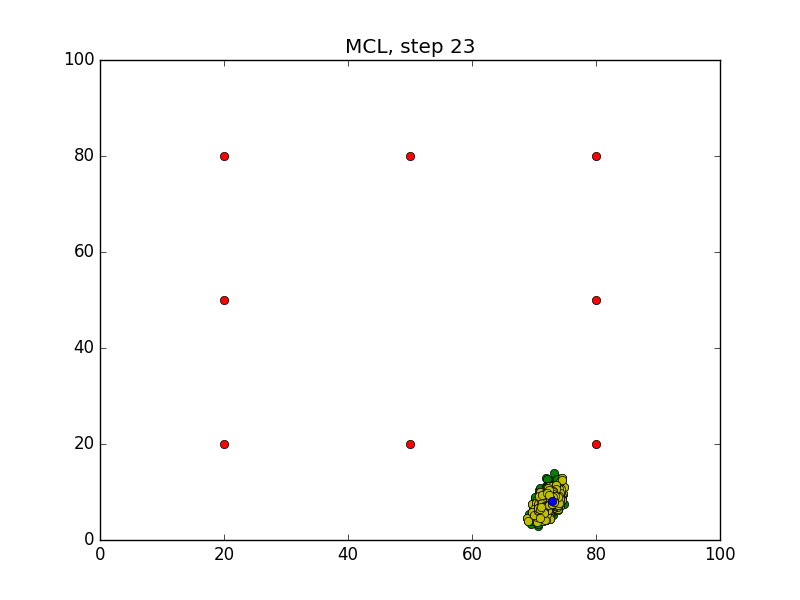
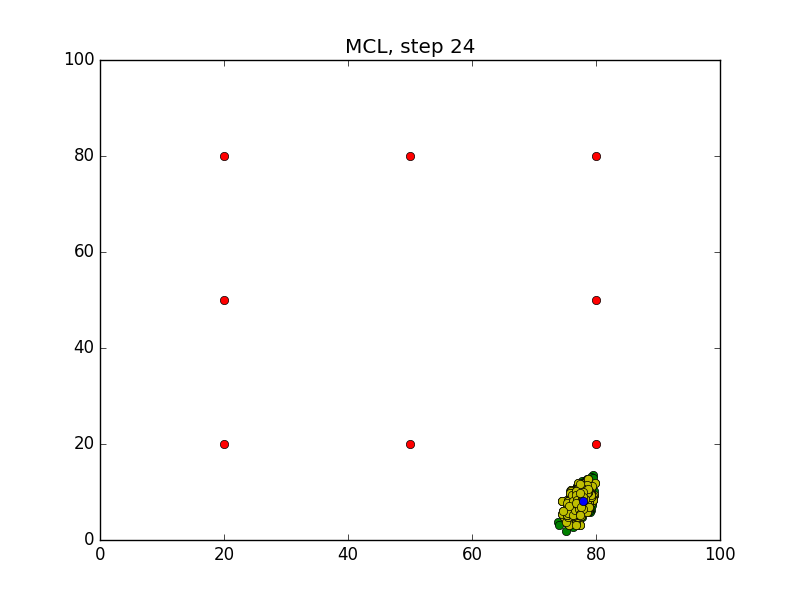
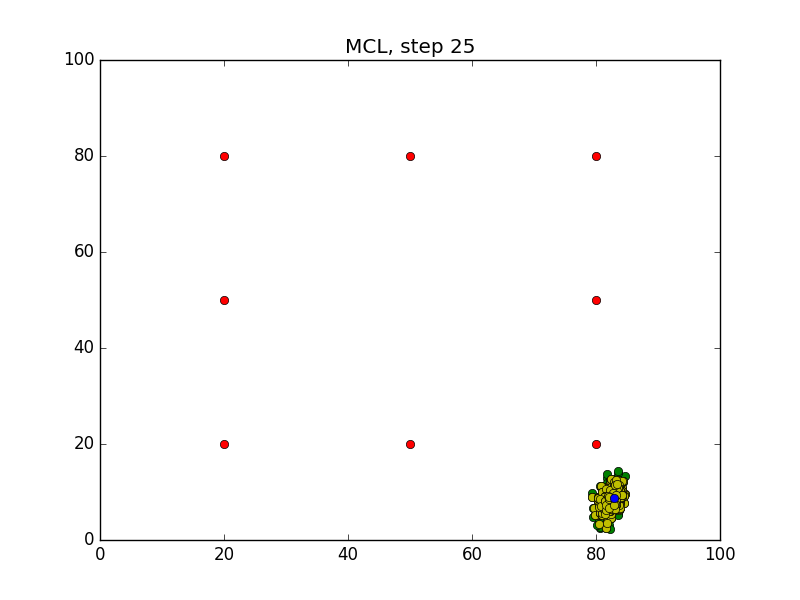
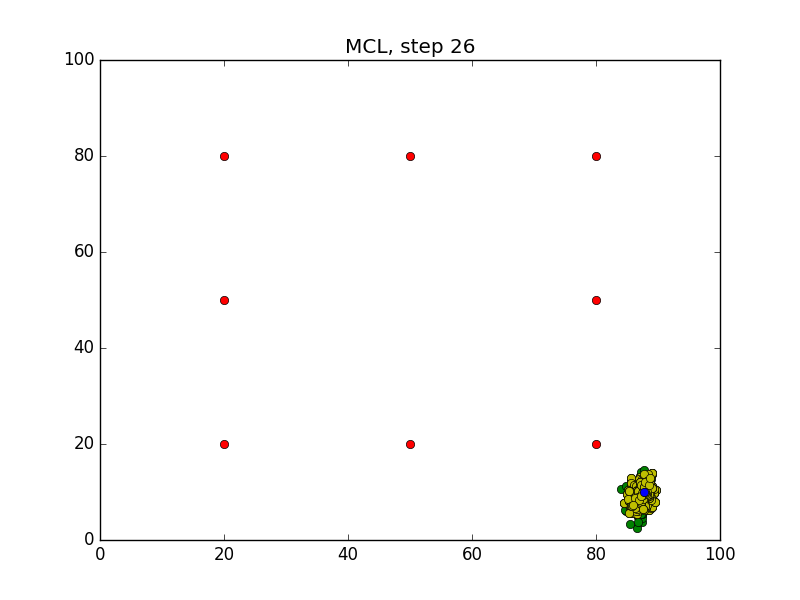
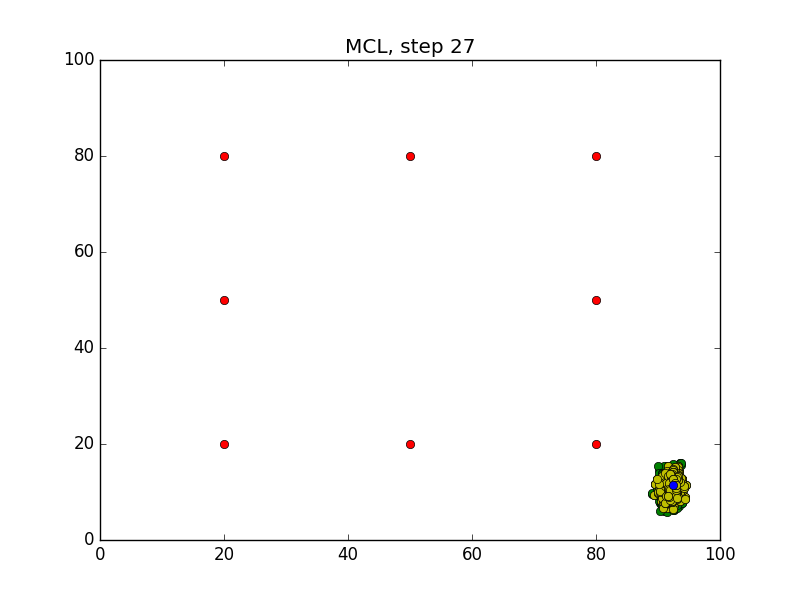
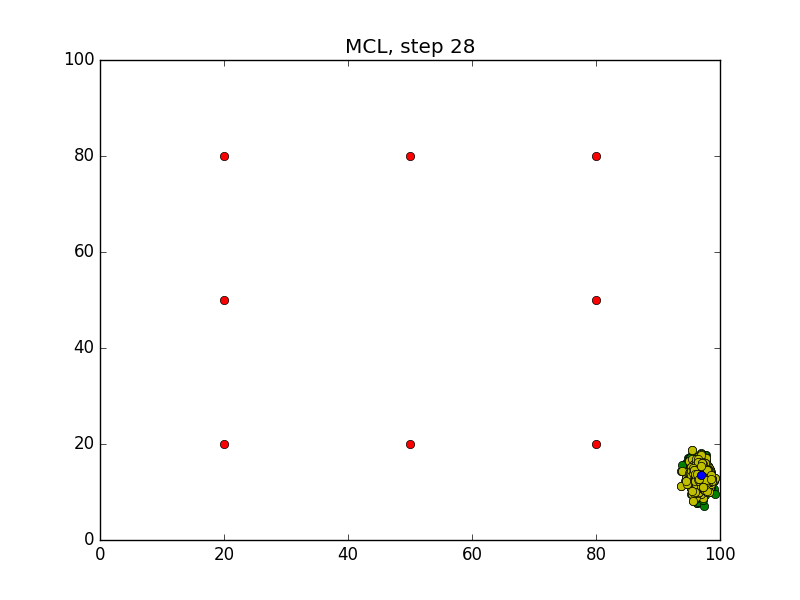
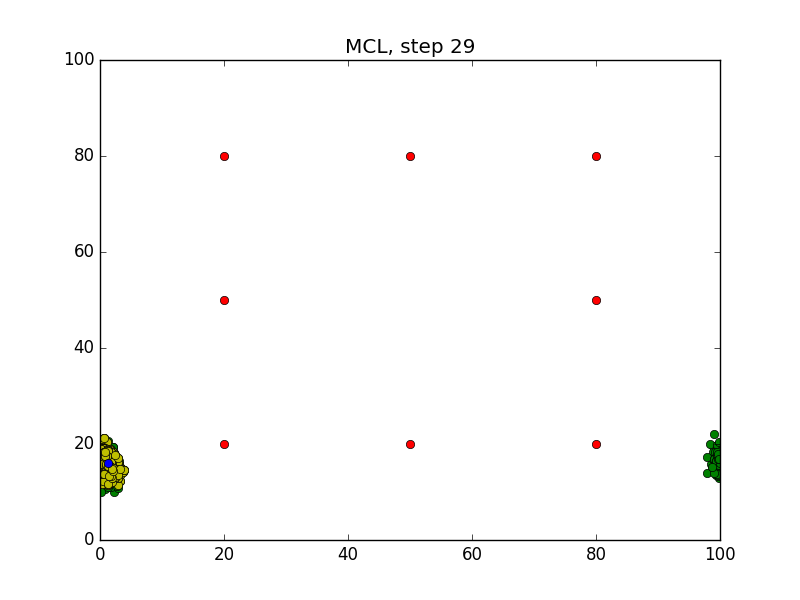
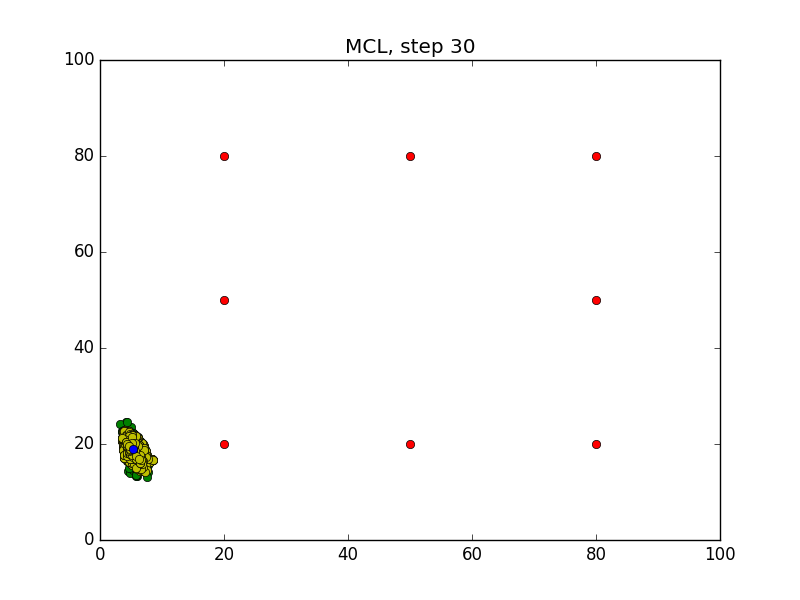
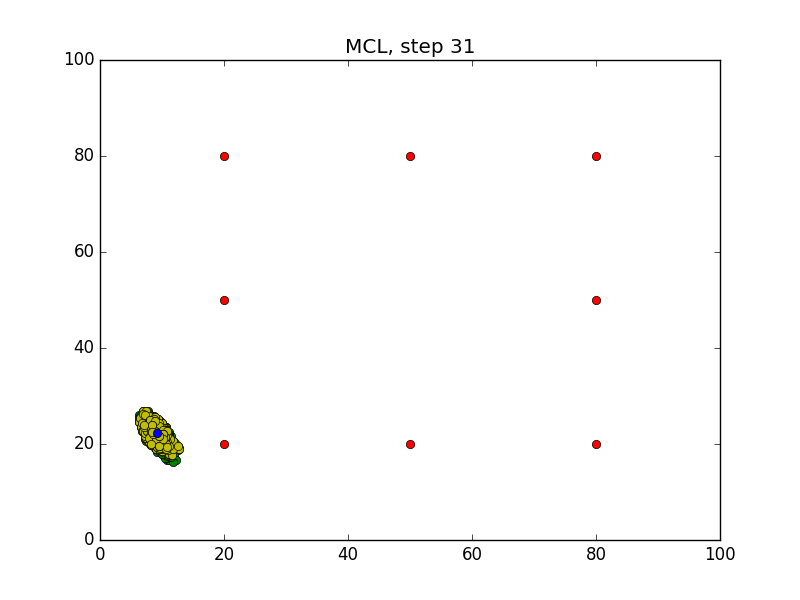
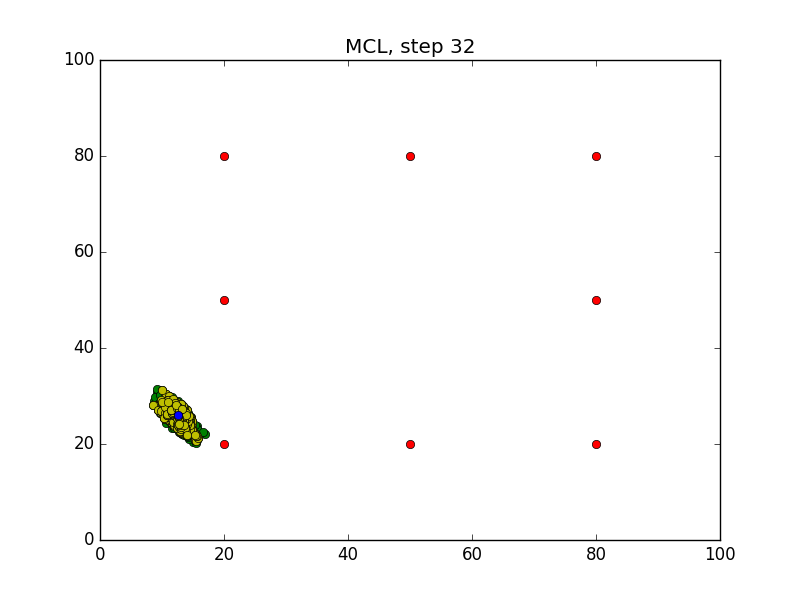
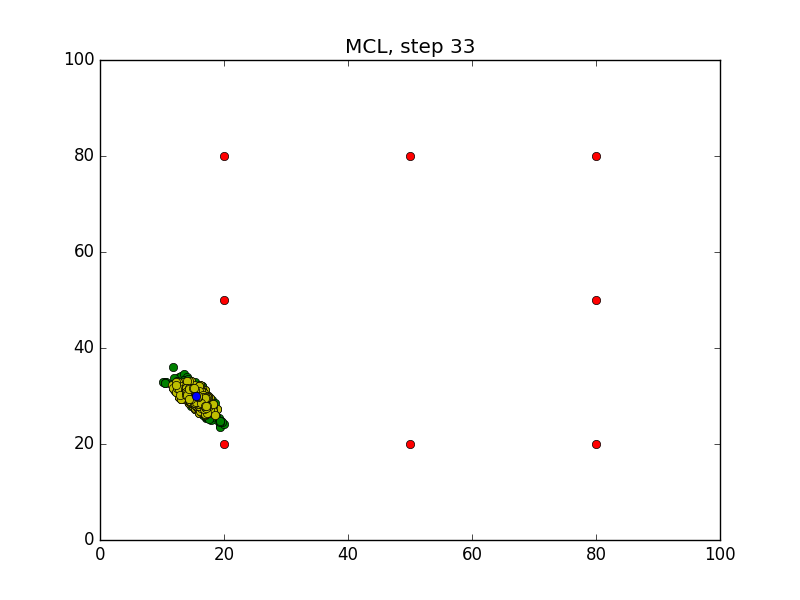
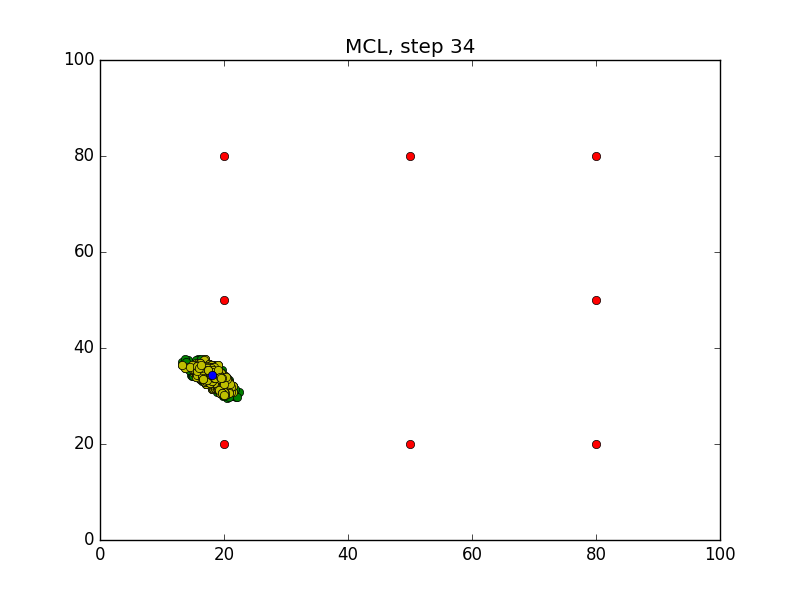
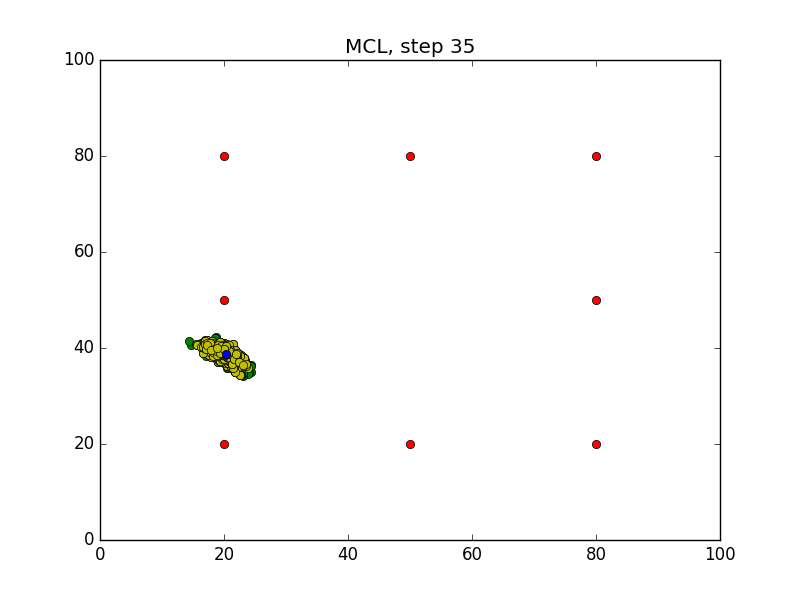
Links
Further details about MCL are found in the paper of Sebastian Thrun et al.
Reference
This post is a summary of the MCLLab from the Robotics Nanodegree of Udacity




Comments