Localization answers the following question:
Where is a car in a given map with a specified accuracy, about 10 cm or less.
GPS is commonly used to find a car with respect to the given map. However, GPS on its own is not precise enough. Most of the time GPS has an accuracy of a width of a lane, about one to three meters. Sometimes it can even be as broad as 10 to 50 meters.
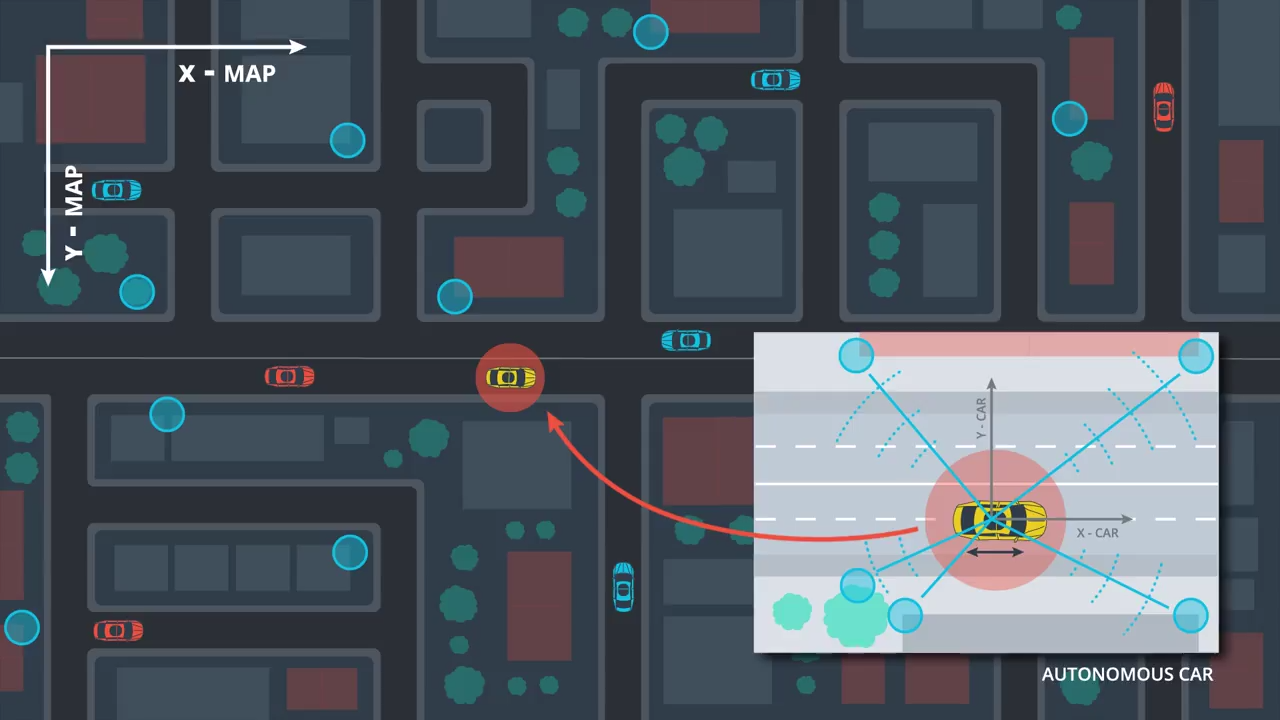
To improve the localization reliability other onboard sensors of the self-driving vehicle are utilized in combination with a detailed map. With the onboard sensor it is possible to measure distances to static obstacles, like trees poles or walls, which can be part of the map. These distances are measured in the local coordinate system of the vehicle.
To estimate where the car is in the map it is necessary to match the observations with the map information. This results in a transformation between both coordinates systems, the local car coordinate system and the coordinate system of the map.
The localization issue is solved if it is possible to estimate this transformation.
To sum up:
Onboard sensors are used to estimate a transformation between measurements and a given map.




Comments