The Facade Pattern provides a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem. Facade defines a higher-level interface that makes the subsystem easier to use.
The Facade Pattern is used when you need to simplify and unify a large interface or complex set of interfaces. It alters an interface to simplify it and thereby hides all the complexity of one or more classes behind a clean facade, hence its name. A facade decouples a client from a complex subsystem and to implement it we compose the facade with its subsystem and use delegation to perform the work of the facade. For a complex subsystem it can be helpful to implement more than one facade. Thereby we try to keep sybsystems adhering to the Principle of Least Knowledge as well. If this gets too complex and too many friends are intermingling, we can introduce additional facades to form layers of subsystems.
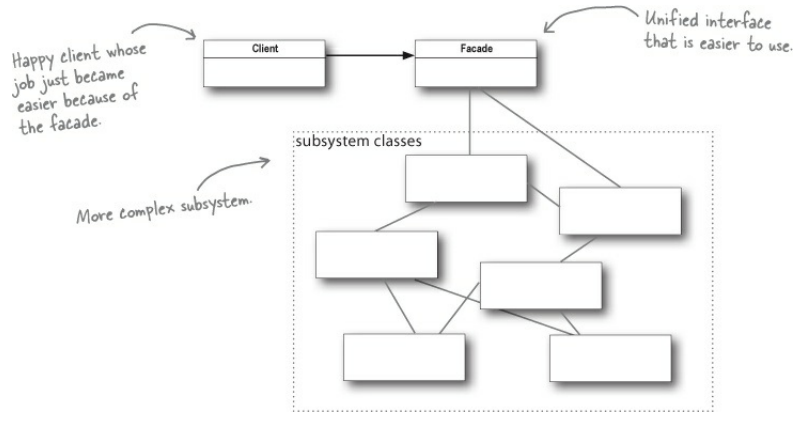
The components of the complex subsystem can be upgraded/changed without affecting the client.
The client usually has only one friend: the Facade class,
which follows the Principle of Least Knowledge:
In OO programming, having only one friend is a good thing.
This pattern is similar to the Adapter Pattern and the Decorator Pattern. An adapter wraps an object to change its interface, a decorator wraps an object to add new behaviors and responsibilities, and a facade “wraps” a set of objects to unify and simplify.
The following example shows a home theater with multiple classes, acting as devices of the home theater that interact with each other and are connected to the Amplifier that is defined later:
For example, we have a Tuner to listen to the radio that can set the mode (AM, FM) and the frequency:
public class Tuner {
String description;
Amplifier amplifier;
double frequency;
public Tuner(String description, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void setFrequency(double frequency) {
System.out.println(description + " setting frequency to " + frequency);
this.frequency = frequency;
}
public void setAm() {
System.out.println(description + " setting AM mode");
}
public void setFm() {
System.out.println(description + " setting FM mode");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}To watch movies a DvdPlayer is connected to the Amplifier:
public class DvdPlayer {
String description;
int currentTrack;
Amplifier amplifier;
String movie;
public DvdPlayer(String description, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.description = description;
this.amplifier = amplifier;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void eject() {
movie = null;
System.out.println(description + " eject");
}
public void play(String movie) {
this.movie = movie;
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " playing \"" + movie + "\"");
}
public void play(int track) {
if (movie == null) {
System.out.println(description + " can't play track " + track + " no dvd inserted");
} else {
currentTrack = track;
System.out.println(description + " playing track " + currentTrack + " of \"" + movie + "\"");
}
}
public void stop() {
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " stopped \"" + movie + "\"");
}
public void pause() {
System.out.println(description + " paused \"" + movie + "\"");
}
public void setTwoChannelAudio() {
System.out.println(description + " set two channel audio");
}
public void setSurroundAudio() {
System.out.println(description + " set surround audio");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}Another device that is connected to the Amplifier is the CdPlayer:
public class CdPlayer {
String description;
int currentTrack;
Amplifier amplifier;
String title;
public CdPlayer(String description, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.description = description;
this.amplifier = amplifier;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void eject() {
title = null;
System.out.println(description + " eject");
}
public void play(String title) {
this.title = title;
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " playing \"" + title + "\"");
}
public void play(int track) {
if (title == null) {
System.out.println(description + " can't play track " + currentTrack +
", no cd inserted");
} else {
currentTrack = track;
System.out.println(description + " playing track " + currentTrack);
}
}
public void stop() {
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " stopped");
}
public void pause() {
System.out.println(description + " paused \"" + title + "\"");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}Each of the devices defined so far are connected with the Amplifiler:
public class Amplifier {
String description;
Tuner tuner;
DvdPlayer dvd;
CdPlayer cd;
public Amplifier(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void setStereoSound() {
System.out.println(description + " stereo mode on");
}
public void setSurroundSound() {
System.out.println(description + " surround sound on (5 speakers, 1 subwoofer)");
}
public void setVolume(int level) {
System.out.println(description + " setting volume to " + level);
}
public void setTuner(Tuner tuner) {
System.out.println(description + " setting tuner to " + dvd);
this.tuner = tuner;
}
public void setDvd(DvdPlayer dvd) {
System.out.println(description + " setting DVD player to " + dvd);
this.dvd = dvd;
}
public void setCd(CdPlayer cd) {
System.out.println(description + " setting CD player to " + cd);
this.cd = cd;
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}To actually watch a movie we need a Projector and a Screen that can be moved up() or down():
public class Projector {
String description;
DvdPlayer dvdPlayer;
public Projector(String description, DvdPlayer dvdPlayer) {
this.description = description;
this.dvdPlayer = dvdPlayer;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void wideScreenMode() {
System.out.println(description + " in widescreen mode (16x9 aspect ratio)");
}
public void tvMode() {
System.out.println(description + " in tv mode (4x3 aspect ratio)");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}Here is the definition of the Screen class:
public class Screen {
String description;
public Screen(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void up() {
System.out.println(description + " going up");
}
public void down() {
System.out.println(description + " going down");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}To watch a movie we also want to dim the lights:
public class TheaterLights {
String description;
public TheaterLights(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void dim(int level) {
System.out.println(description + " dimming to " + level + "%");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}Finally to enjoy the movie even more, we have a popcorn popper:
public class PopcornPopper {
String description;
public PopcornPopper(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void pop() {
System.out.println(description + " popping popcorn!");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}It is possible to interact with those subsystems directly without using a Facade.
This means that we get low-level access to the complex subsystem.
However, for tasks such as watching a movie or listening to the readio,
the Facade Pattern provides a unified and simple interface with the following HomeTheaterFacade class,
that allows watching a movie with a single method watchMovie(String movie) and shut everything down afterwards in the correct order with endMovie():
public class HomeTheaterFacade {
Amplifier amp;
Tuner tuner;
DvdPlayer dvd;
CdPlayer cd;
Projector projector;
TheaterLights lights;
Screen screen;
PopcornPopper popper;
public HomeTheaterFacade(Amplifier amp,
Tuner tuner,
DvdPlayer dvd,
CdPlayer cd,
Projector projector,
Screen screen,
TheaterLights lights,
PopcornPopper popper) {
this.amp = amp;
this.tuner = tuner;
this.dvd = dvd;
this.cd = cd;
this.projector = projector;
this.screen = screen;
this.lights = lights;
this.popper = popper;
}
public void watchMovie(String movie) {
System.out.println("Get ready to watch a movie...");
popper.on();
popper.pop();
lights.dim(10);
screen.down();
projector.on();
projector.wideScreenMode();
amp.on();
amp.setDvd(dvd);
amp.setSurroundSound();
amp.setVolume(5);
dvd.on();
dvd.play(movie);
}
public void endMovie() {
System.out.println("Shutting movie theater down...");
popper.off();
lights.on();
screen.up();
projector.off();
amp.off();
dvd.stop();
dvd.eject();
dvd.off();
}
public void listenToCd(String cdTitle) {
System.out.println("Get ready for an audiopile experence...");
lights.on();
amp.on();
amp.setVolume(5);
amp.setCd(cd);
amp.setStereoSound();
cd.on();
cd.play(cdTitle);
}
public void endCd() {
System.out.println("Shutting down CD...");
amp.off();
amp.setCd(cd);
cd.eject();
cd.off();
}
public void listenToRadio(double frequency) {
System.out.println("Tuning in the airwaves...");
tuner.on();
tuner.setFrequency(frequency);
amp.on();
amp.setVolume(5);
amp.setTuner(tuner);
}
public void endRadio() {
System.out.println("Shutting down the tuner...");
tuner.off();
amp.off();
}
}To watch a movie we could use the components of the subsystem directly (hard way) by doing the following steps:
- Turn on the popcorn popper
- Start the popper popping
- Dim the lights
- Put the screen down
- Turn the projector on
- Set the projector input to DVD
- Putth eprojector on wide-screen mode
- Turn the sound amplifier on
- Set the amplifier to DVD input
- Set the amplifier to surround sound
- Set the amplifier volume to medium (5)
- Turn the DVD palyer on
- Start the DVD player playing
We would have to create the required devices ourselfs and then call each of its method in the correct order:
popper.on(); // Turn on the popcorn popper
popper.pop(); // Start popping
lights.dim(10); // Dim the light to 10%
screen.down(); // Put the screen down
// Turn on the projector and put it in wide screen mode for the movie
projector.on();
projector.setInput(dvd);
projector.wideScreenMode();
amp.on(); // Turn on the amp,
amp.setDvd(dvd); // set it to DVD,
amp.setSurroundSound(); // put it in surround sound mode,
amp.setVolume(5); // and set the volume to 5
dvd.on(); // Turn on the DVD player
dvd.play(movie); // and finally, play the movie.As we can see, this involves six different classes.
Using the HomeTheaterFacade gives us a single method to achieve the same:
public class HomeTheaterTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Amplifier amp = new Amplifier("Top-O-Line Amplifier");
Tuner tuner = new Tuner("Top-O-Line AM/FM Tuner", amp);
DvdPlayer dvd = new DvdPlayer("Top-O-Line DVD Player", amp);
CdPlayer cd = new CdPlayer("Top-O-Line CD Player", amp);
Projector projector = new Projector("Top-O-Line Projector", dvd);
TheaterLights lights = new TheaterLights("Theater Ceiling Lights");
Screen screen = new Screen("Theater Screen");
PopcornPopper popper = new PopcornPopper("Popcorn Popper");
HomeTheaterFacade homeTheater =
new HomeTheaterFacade(amp, tuner, dvd, cd,
projector, screen, lights, popper);
homeTheater.watchMovie("Raiders of the Lost Ark");
homeTheater.endMovie();
}
}The output of the program is:
$ java HomeTheaterTestDrive
Get ready to watch a movie...
Popcorn Popper on
Popcorn Popper popping popcorn!
Theater Ceiling Lights dimming to 10%
Theater Screen going down
Top-O-Line Projector on
Top-O-Line Projector in widescreen mode (16x9 aspect ratio)
Top-O-Line Amplifier on
Top-O-Line Amplifier setting DVD palyer to Top-O-Line DVD Player
Top-O-Line Amplifier surround sound on (5 speakers, 1 subwoofer)
Top-O-Line Amplifier setting volume to 5
Top-O-Line DVD Player on
Top-O-Line DVD Player playing "Raiders of the Lost Ark"
Shutting movie theater down...
Popcorn Popper off
Threater Ceiling Lights on
Theater Screen going up
Top-O-Line Projector off
Top-O-Line Amplifier off
Top-O-Line DVD Player stopped "Raiders of the Lost Ark"
Top-O-Line DVD Player eject
Top-O-Line DVD Player off
Comments